DNS HIJACKING
What is DNS Hijacking ?
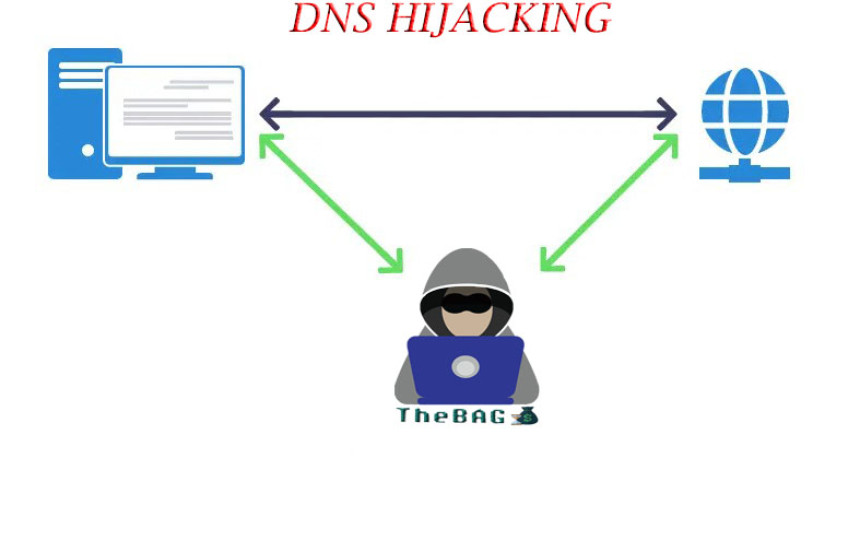
Domain name server (DNS) hijacking is also called DNS redirection. It is a type of DNS attack in which DNS queries are resolved incorrectly in order to redirect users to malicious sites unexpectedly. During the attack, the attacker can install malware on users' computers, hijack routers, interrupt or hack DNS communication.
DNS hijacking can be used for pharming or phishing.
Many Internet Service Providers (ISPs) use some form of DNS hijacking to hijack DNS requests, collect statistics, and return advertisements when accessing unknown domains.
Some governments and administrators use DNS hijacking for censorship so that users are directed only to government-authorized sites.
Types of DNS Hijacking Attacks
There are four basic types of DNS redirection or hijacking :
- Local DNS hijack :
Attackers install Trojan software on the victim's computer and change local DNS settings to redirect to malicious websites.
- Router DNS Hijack :
Many routers have default passwords or firmware vulnerabilities. Therefore, Attackers can take control of a router and thus overwrite DNS settings, affecting all users connected to the router.
- Man in the middle DNS attack :
In this type of attack, which is one of the most preferred methods, attackers capture the user's DNS requests and interrupt the communication between the user and the DNS server and set IP addresses with different targets that mark malicious sites, that is, direct them to their own DNS server.
- Rogue DNS Server :
In this method, the attacker hacks the DNS server and changes DNS records to redirect DNS requests to malicious sites.
Now that we have knowledge about DNS hijacking i will talk about DNS Spoofing attacks and how to protect against in next post .





